What is the HCl Full Form In Chemistry
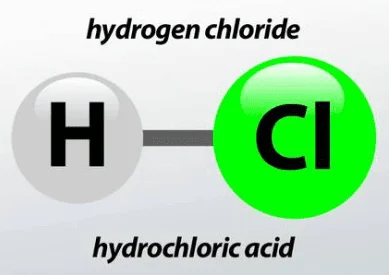
The HCL full form in Chemistry is Hydrogen Chloride.- It is a hydrogen halide, where Cl is the halide
- It is in the form of gas at room temperature and the chemical formula is HCl
- HCl gas dissolves in water, the solution of HCl in water is called hydrochloric acid
- The hydrochloric acid formula is commonly written as HCl but scientifically it is denoted by HCl(aq), where aq full form in chemistry is aqueous i.e water
- It is available commercially in the concentration from 10 to 34 percent
- The HCL(aq) is also known as muriatic acid, spirits of salt, hydronium chloride and chlorhydric acid
- The IUPAC name of HCL acid is Chlorane
- HCL gas in contact with body tissues forms corrosive hydrochloric acid
- Inhalation of HCL gas causes
- Choking
- Coughing
- Inflammation of nose throat etc
- HCl can severely burn skin and damage eye permanently
Hydrochloric Acid ph
The pH of hydrochloric acid depends on how much HCL gas is dissolved in water
- A 1 molar HCl solution has a pH of zero
Curious to know what is hydrochloric acid used for? Following are some of the common used of HCl
- Hydrochlorination of rubber
- In preparation of vinyl chloride and alkyl chlorides
- Etching of semiconductors and purification of silicon via trichlorosilane
- Formation of chlorinated and fluorinated organic compounds like
- Freon
- Teflon
- CFCs
- Chloroacetic acid
- PVC
The common household cleaners contain hydrochloric acid
- Scrub toilet bowl
- Bathroom tile cleaner